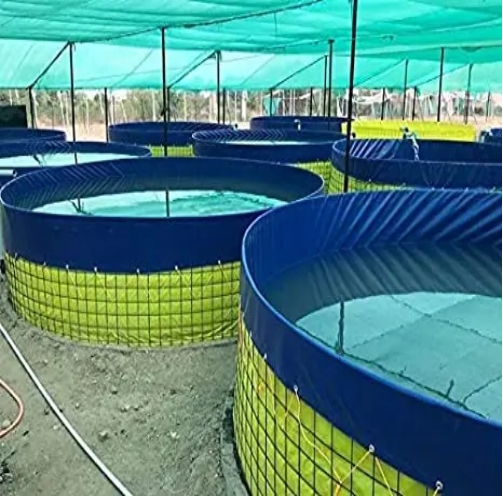
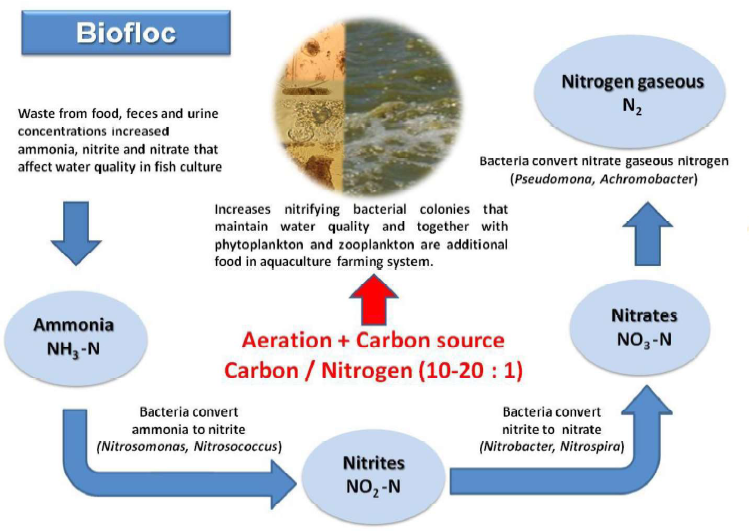


Biofloc fish farming is an innovative and sustainable method of aquaculture that involves the creation and management of a unique aquatic environment where microbial communities develop, providing a natural source of nutrition for the fish. This system reduces the need for water exchange, as the microbial communities consume organic waste, nitrogen, and other compounds, creating a self-sustaining ecosystem. In biofloc fish farming, a carbon source such as molasses or starch is added to the water, promoting the growth of heterotrophic bacteria, which convert the carbon into biomass. This biomass serves as a food source for the fish, which consume the biofloc and the microbial community. The system offers several benefits, including reduced water usage and environmental impact, production of high-quality protein, and economic efficiency. However, it also presents some challenges, including the management of the microbial community and the need for standardized protocols.

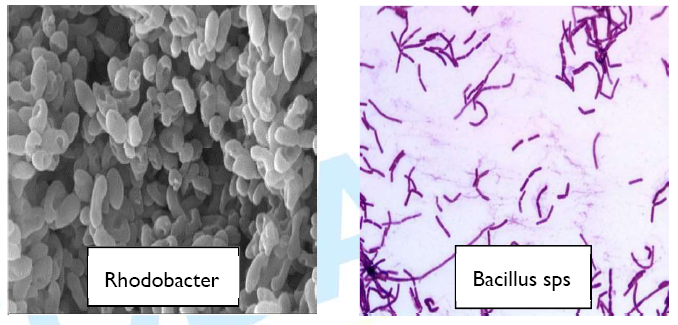
Bio-floc are of two main types. Classification is based on the amount and nature of organic matter and its component organisms, the latter can be bacterial or autotrophic, mainly composed of algae biofloc fish farming near me. The importance of this is that, in both cases, the microorganisms present in the bio-flocs maintain water quality because they decrease nitrogen compounds and are also nutrients for the bacterial and algae. It is important to understand that, depending on the nature of the bio-floc microorganisms, their nutritional quality can vary. This affects the supply of nutrients for the stock organisms in the fish tank.
into high-quality protein. In bio-floc fish farming, a carbon source such as molasses or starch is added to the water, promoting the growth of heterotrophic bacteria, which convert the carbon into biomass. This biomass serves as a food source for the shrimp or fish, which consume the bio-floc and the microbial community. The microbial community is composed of different types of bacteria that work together to create a self-sustaining ecosystem. The bacteria consume the organic waste and convert it into ammonia, which is then converted into nitrite and nitrate by nitrifying bacteria. These compounds are essential for plant growth, and the bio-floc system can be combined with hydroponics or other plant cultivation systems, creating a symbiotic relationship. Benefits of Bio-Floc Fish Farming Bio-floc fish farming offers several benefits compared to traditional aquaculture practices. One of the most significant advantages is the reduction in water exchange. In conventional aquaculture, large amounts of water are required to remove waste and maintain water quality. Bio-floc systems reduce the need for water exchange by up to 90%, reducing water usage and environmental impact. Another significant benefit of bio-floc fish farming is the production of high-quality protein. The microbial community provides a natural source of nutrition for the fish, improving growth rates and reducing the need for external feed. The bio-floc system also creates a healthier environment for the fish, reducing the risk of disease and mortality. Bio-floc fish farming also offers economic benefits, as the system is highly efficient and requires less labor compared to traditional aquaculture. The reduced need for water exchange and external feed reduces operational costs, and the higher yields and faster growth rates result in increased profits. Challenges and Opportunities While bio-floc fish farming offers several benefits, it also presents some challenges and opportunities. One of the primary challenges is the management of the microbial community. The bio-floc system is highly dependent on the microbial community, and the balance between different types of bacteria can be easily disrupted. Careful management is required to ensure optimal water quality and prevent the growth of harmful bacteria. Another challenge is the lack of standardized protocols for bio-floc fish farming. The system is relatively new, and there is a need for standardized guidelines and best practices. This includes the development of monitoring and management protocols for water quality, nutrient levels, and microbial communities. However, the challenges presented by bio-floc fish farming also present opportunities for research and development. The system offers a unique platform for studying microbial ecology, and there is a need for research into the optimal conditions for the growth and development of the microbial community. Conclusion Bio-floc fish farming is a sustainable and innovative aquaculture practice that offers several benefits compared to traditional aquaculture. The system creates a self-sustaining ecosystem that reduces the need for water exchange and external feed, resulting in higher yields and increased profits. However, the system also presents some challenges, including the management of the microbial community and the need for standardized protocols
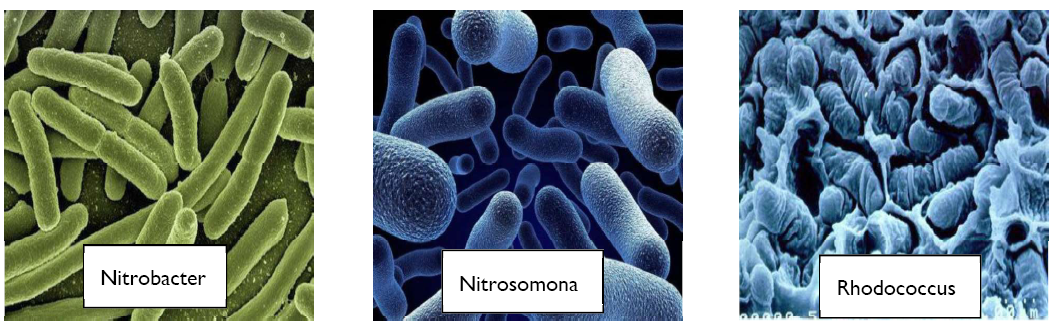
The microorganisms that form the bio-floc and process nitrogen compounds that pollute fish pond water need a source of energy for metabolism. In aquatic bio-floc systems, there are three likely energy sources, depending on the nature of the organisms present in the bio-floc system (bacteria algae aggregations). Biofloc fish farming government subsidy Most important is sunlight, which is the main source of energy for phototrophic microorganisms, such as algae and vascular plants. Solar reception can be controlled or semi-controlled to support the needs of the bio-floc crop and promote any type of bio-floc system. The second source of energy is the forms of inorganic compounds that are used by the microorganisms that oxidize reduced forms of simple compounds, especially nitrogen to obtain energy. In fish farming, by metabolizing organic nitrogen and ammonia, nitrogen is oxidized to nitrite and nitrate. The third source of energy is organic compounds that are transformed by microorganisms that derive energy from the metabolic oxidation of organic carbon and transform it to carbon dioxide. Both chemotrophic and phototrophic microorganisms naturally consume and deplete nitrogen concentrations in the water because of the relatively large quantity of energy sources that are present, but also because this is an indispensable function of the microorganisms. Transformed energy is used to synthesis proteins from the nitrogen sources. Systems for cleaning and wastewater bioremediation, using microalgae and bacteria, is a widely known technology; however, in aquaculture systems, biofloc fish farming cost they should be used with caution because, with microalgae, the efficiency of the system depends directly on solar energy and intensity, which in open systems can be a risk because there is no control over productivity. An excess of primary production leads to constant consumption of oxygen during the night. On cloudy days, productivity will reduce water quality. Biofloc or nitrifying colonies of bacteria in aquaculture requires incorporation of additional carbon sources into the system to adequately reproduce biofloc and maintain high density because carbohydrates in the system may be insufficient. Some of the main sources of carbon that can be used in aquaculture crops are: glycerol and sodium acetate, sugar, tapioca flour, wheat flour, and molasses. Use depends directly on the local costs of these products. For a biofloc system to operate efficiently, it is best to maintain a C/N ratio between 10:1 and 20:1. The amount of carbon depends on several factors, including: water quality, physiology and growing body density of the stock, quality and quantity of food to be cultivated, and solubility of the carbon SAJAN M GUPTA Mobile & WhatsApp No +91 94370-20831, +91 82870-93301 Page | 6 source. The carbon additive must be continuously monitored to ensure that the system is functioning properly.
Biofloc technology provides more efficient and sustainable aquaculture by reducing environmental impacts. One major advantage is reducing the volume of water required by the system during cultivation biofloc fish farming cost Biofloc in the cultivation system uses the initial water volume throughout the production cycle and needs additional water only to replace water lost by evaporation, leakage, or to remove organic material during production. Biofloc fish farming government subsidy The biofloc microorganisms serve as natural food, depending on the eating habits of the stock species. This will reduce consumption of artificial food and lead to more efficient conversion of food. Bio-floc is more than a supplemental source of nutrients in aquatic systems. It brings economic benefits during production and enables more efficient use of resources, given that the main source of protein during production is fish meal.